- Home
- World War I
- Civics & Government
- Ideologies (Types of Government)
- Governor General: Head of State vs Head of Government
- Parliament, House of Commons and Senate
- The Executive Branch and Cabinet
- The Legislative Branch
- The Judicial System
- Representative Democracy, Constitutional Monarch & Federal State
- Federal, Provincial, Shared & Municipal: Government Responsibiliites
- The Constitution
- The Electoral System: Political Parties
- The Political Spectrum
- The Election Process: Who Can Vote?
- Majority & Minority Government
- First Past the Post vs Proportional, Representation vs Prefrential Ballot
- Influences on the Government
- Human Rights in Canada
- Provincial Human Rights Legislation
- Canada in the 1920's
- Winnipeg General Strike
- Regionalism In Canada
- The King-Byng Crisis
- The Balfour Report
- USA Investment and Branch Plants
- Prohibition and Bootlegging
- Women in the Roaring 20's
- Improved Mobility and Communicationss
- Art and Entertainment in the 1920's
- Minorities in the 1920
- Black Tuesday: The Stock Market Crash of 1929
- Canada in the 1930s
- Causes of the Depression
- Pogey - Government Payment
- Government Stops - Immigration 1931
- Prime Minister King and The Depression
- Prime Minster Bennett and The Depression
- Protests Against the Depression
- The J.S. Woodsworth and the CCF
- Maurice Duplessis and the Union Nationale
- Equalizations Payments
- The Rise of the Dictaorships
- The Policy of Appeasement
- Canada in World War II
- Canada and the Cold War
- Life in Canada during the Cold War
- The Marshall Plan
- Baby Boomers
- Social Welfare and International Aid
- The CBC, CRTC and Rise of Television
- The Age of the Automobile
- Era of Protest and Women’s Liberation Movement
- Expo ‘67 and Canada’s Centennial
- Trudeaumania
- Prime Ministers of the Era: St. Laurent, Diefenbaker, Pearson, Trudeau
- The Avro Arrow
- The St. Lawrence Seaway
- NORAD
- Inflation and OPEC
- The National Energy Program
- The 1972 Summit Series
- Citizenship Act of 1976 and Immigration Act of 1978
- From Mulroney to Present
- The Cold War Ends: Détente, SALT I and II, Glasnost, Perestroika
- The Falling of the Berlin Wall, 1989 and Breakup of Soviet Union
- Prime Minister Mulroney: FTA, NAFTA, Deficits and GST
- Operation Desert Storm
- Peacekeeping: Somalia (1992) and Rwanda (1994)
- NATO, Kosovo and International Criminal Court (ICC)
- Kim Campbell, The Montreal Massacre and Women in Canada
- Irene Murdoch and Rosemary Brown
- 1993: Jean Chretien, Bloc Quebecois and Reform Party
- Public Health Care: Two Tier System
- Canadarm and SDI
- Pacific Salmon Wars and the Pacific Salmon Treaty
- Terry Fox, Rick Hansen, Craig Kielburger, David Suzuki
- The War on Terror and Land Mines
- The Group of Eight (G8)
- The Environmental Movement and the Kyoto Accords
- Refugees and Boatpeople
- CIDA, ODA, International Aid
- Quebec and Aboriginal Issues in Canada
- Native Suffrage, 1960 and the White Paper, 1969
- Land Claims
- Oka Standoff, 1990
- The Nisga’a Treaty
- Nunavut
- Maurice DuPlessis and the Union Nationale
- The Quiet Revolution
- The FLQ and the October Crisis, 1970
- The War Measures Act, 1970
- The Parti Quebecois and Bill 101
- Referendum, 1980
- Constitution Act of 1982
- Meech Lake Accord, 1987
- Charlottetown Accord, 1992
- Bloc Quebecois and Referendum 1995
- Potential Impacts of Separation
- Human Geography: Population, Living Standards, Urbanization
- Population: Canada and the World
- Census, Population Rates and the Rule of 70
- Demographics and Migration
- Population Pyramids
- Living Standards
- Poverty (and how to measure it)
- The Poverty Trap
- The Effects of Poverty on Women and Children
- The Health Crisis: Fresh Water and Epidemics
- Urbanization
- Function and Form in Cities
- The Use of Automobiles in Cities
- Land Uses in Cities
- Sustainability in Cities
- Aquifiers and Surface Water
- The Hole in the Ozone Layer
- Global Warming
- Agriculture and Soils
- Declining Forests
View 1974 Summit Series and over 3,000,000 other topics on Qwiki.
_"Napoleon didn't take
Moscow, the Nazis got within 21 miles in 1943, but in a war of a different
kind, Team Canada conquered Moscow." - journalist Dick Beddoes.
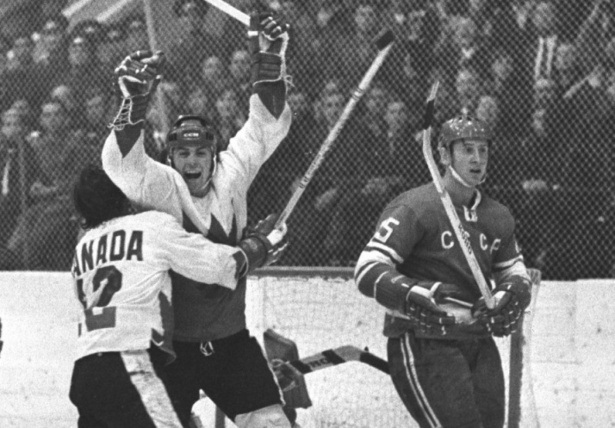
The 1972 Summit Series
A new approach to world affairs during the Cold War
Canada wanted to compete with the communist (ping pong diplomacy) in sporting events
Four games in Canada and four in Russia
Canada wins the series on a goal with 30 seconds left by Paul Henderson
Canada would later boycott the 1980 olympics in Moscow as a result of the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
The Soviets would do the same in Los Angeles in 1984 (the most medals Canada ever got)
Canada wanted to compete with the communist (ping pong diplomacy) in sporting events
Four games in Canada and four in Russia
Canada wins the series on a goal with 30 seconds left by Paul Henderson
Canada would later boycott the 1980 olympics in Moscow as a result of the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
The Soviets would do the same in Los Angeles in 1984 (the most medals Canada ever got)
Summary
The 1972 Summit Series was a large event for Canada thanks to the goal scored by Paul Henderson against the Russians in the last 30 seconds on the game. Never has a single sporting moment meant so much to so many Canadians a sense of unparalleled nationalism. This was a large step after WWII because it was the first approach to world events.